
What is a Nuclear Medicine Bone Scan? What To Expect
Did you know that small amounts of radioactive material can help reveal big problems in bone health?
A nuclear medicine bone scan is a specialised imaging test used to detect a number of bone-related conditions, from fractures and infections to cancer. Using a small amount of radioactive tracer can provide detailed images of the bones and identify any problems with a patient’s health.
We know this can sound like a complicated procedure and can even be a bit anxiety-inducing. Don’t worry; it’s a safe and reliable type of medical imaging, and we’re here to help.
In this article, we’ll give you a clear and comprehensive understanding of what a bone scan involves, why it’s so important in medical diagnosis, and what you can expect during and after the procedure.
Whether you’re managing bone pain or simply monitoring your health, this guide will help you understand the process and even highlight the benefits of nuclear medicine in bone care.
Preparation for a Bone Scan
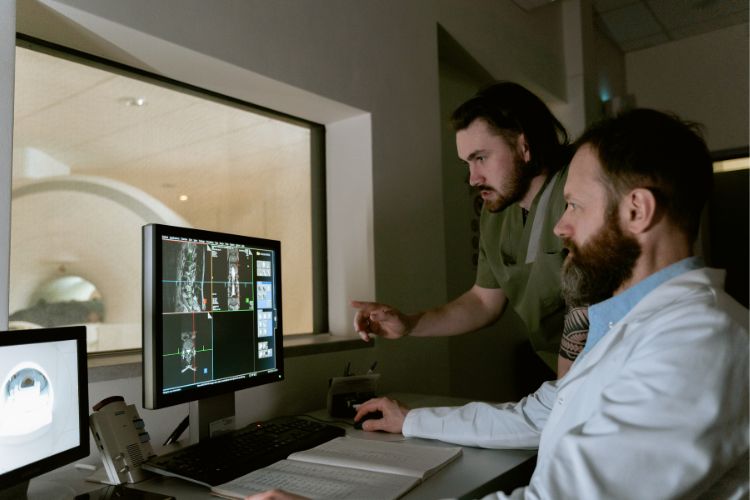

Preparing for a bone scan is very straightforward, but there are a few important things you’ll need to keep in mind:
1. No Special Dietary Restrictions:
There are no dietary restrictions prior to a bone scan. You can eat and drink as usual unless your doctor instructs otherwise.
2. Stay Hydrated:
It’s important to drink plenty of water before the scan. Hydration helps the body absorb the tracer used in the scan more effectively and eliminate the tracer from the body more quickly.
3. Informing Healthcare Providers:
-
- Medical Conditions: Let your doctor or technologist know about any medical conditions.
- Current Medications: Disclose any medications you’re taking, but rest assured they most likely won’t affect the scan.
4. Wear Comfortable Clothing:
It’s recommended that you wear comfortable clothing and easily removable jewellery and accessories.
Remember, the nuclear medicine technologist and our staff at PRP are here to guide you through the process. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and share your concerns during the lead-up to the procedure.
Arrival at the Imaging Facility
When you arrive at the imaging facility for your bone scan, here’s what you can expect:
1. Check-In Process:
-
- Upon arrival, you’ll check in at the reception desk.
- Be prepared to show identification and provide any necessary documents, such as your Medicare card/private health insurance information and referral.
- If you’re a new PRP patient, you’ll likely need to fill out some paperwork, including a consent form and medical history.
2. Pre-Scan Preparations:
-
- As we mentioned earlier, it’s best to wear comfortable clothing that’s easy to remove.
- The practice will provide you with a place to store your personal items, including your clothing and any jewellery.
The staff at PRP are there to assist you and make your experience as smooth as possible. Feel free to reach out to them anytime you have questions or concerns.
Administration of Radiopharmaceuticals
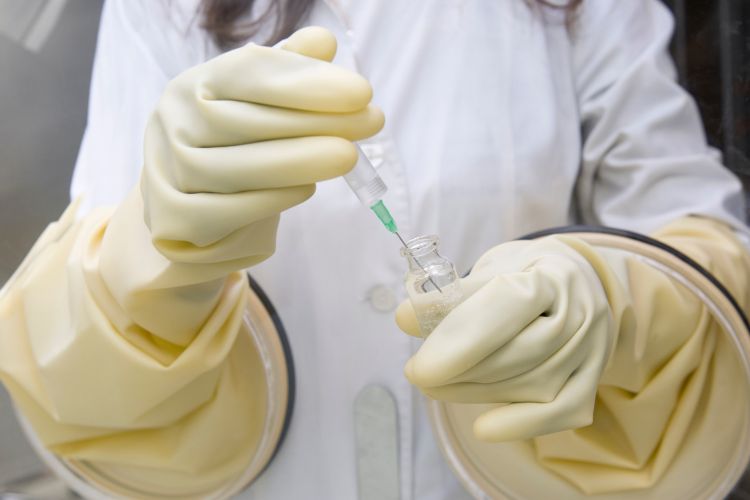

Radiopharmaceuticals play a key role in a nuclear medicine bone scan:
1. Method of Administration:
-
- The radiopharmaceutical is administered via an injection into a vein, usually in your arm.
- The process is similar to a routine blood test, and it’s usually quick.
2. Role in Imaging:
-
- Once injected, the radioactive tracer enters the bloodstream and travels around your body. It’s absorbed (taken up) by the bones over a roughly 2-hour period.
- The radioactive tracer used for bone scans is attracted to the bones and any of their abnormalities. This is what makes them so accurate and crucial for bone imaging.
- The nuclear medicine physician will later interpret these images, focusing on areas where high amounts of the tracer have accumulated.
3. Radiation Exposure:
-
- Rest assured, the amount of radiation in bone scans is minimal and considered safe for all patients.
- Radiation exposure from these tests is very carefully controlled and monitored to ensure patient safety.
4. Importance in Diagnosis and Treatment:
-
- The precise targeting of these radiopharmaceuticals helps doctors identify specific bone issues. It guides both diagnosis and treatment plans.
The administration of radiopharmaceuticals is a vital step in nuclear medicine scans. It provides doctors with essential data for accurate medical interpretation and care.
Imaging Session
The imaging session of a nuclear medicine bone scan involves several steps:
1. Setting Up the Scan:
-
- Depending on the pathology that you’re visiting PRP for, we will set you up on a bed, administer your injection, and take some images immediately.
- Once we’ve looked at the blood flow to the area in question, we’ll get you up and send you away for 2–4 hours (with a return time). During this time, the injection travels around your body and is absorbed by your bones. Once you return, we’ll take the delayed images of your system.
- For a bone scan, we use a gamma camera to detect the radioactive tracer in your body.
2. How the Equipment Works:
-
- The gamma camera moves around you without touching you.
- It captures gamma rays emitted by the technetium in your bones, transforming them into an image.
3. During the Scan:
-
- You’ll need to stay as still as possible to ensure clear and accurate images.
- The technologist may need to reposition you to capture different angles and spots.
4. Identifying Abnormalities:
-
- Areas with increased radioactivity — such as tumours, infection, or areas of disease — show up as ‘hot spots’ on the image.
The session typically takes 30 to 60 minutes. It’s a safe and painless procedure that’s crucial for detecting various bone conditions.
Duration and Comfort During the Procedure
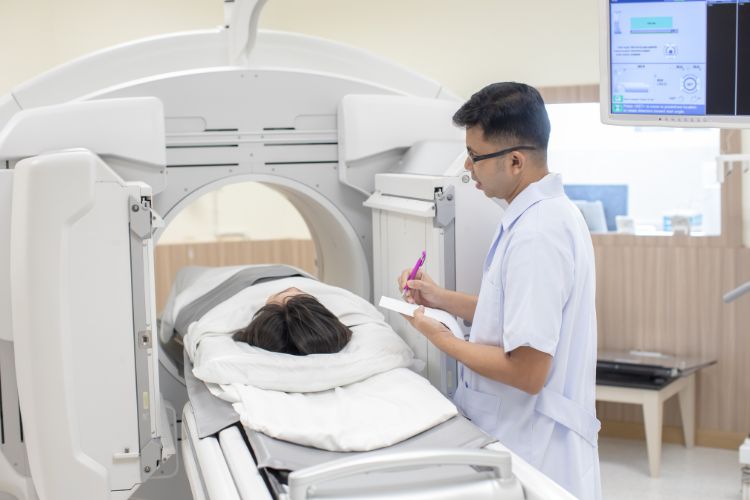
It’s important to understand the duration and comfort aspects of a nuclear medicine bone scan:
1. Typical Duration:
-
- This is a 2-part scan — the injection and the delayed imaging. The entire bone scan process, including both the injection and imaging, typically takes 3–5 hours.
- The actual scanning time usually ranges from 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the area of your body being examined.
2. Ensuring Patient Comfort:
-
- Examination tables are designed for comfort, allowing people to relax during the scan.
- The procedure is non-invasive and painless, similar to having a CT scan, but typically with no feelings of discomfort.
3. Additional Considerations:
-
- Patients are encouraged to empty their bladder before the scan, both for comfort and to remove any unabsorbed tracer from their body.
- You can resume normal activities immediately after the procedure unless your doctor specifies otherwise.
- There are virtually no risks of damage from the scan, making it safe for both adults and children (however, women who are or may be pregnant should always consult with their doctor first).
4. Patient Positioning:
-
- During the scan, you might be asked to change positions to get clear images of different bones. Staff will assist you to ensure you remain comfortable throughout the whole procedure.
This painless and non-invasive process is designed to maximise patient comfort, all while providing critical diagnostic information to improve or maintain your bone health.
Post-Scan Instructions and Follow-Up
After completing your nuclear medicine bone scan, here’s what you need to know:
1. Post-Scan Guidelines:
-
- We recommend that you drink plenty of water to help flush the radioactive material from your body. This reduces any risk of side effects.
2. Safety and Side Effects:
-
- The scan has no significant side effects. However, if you notice any changes in your condition or an unusual response, inform your healthcare provider as soon as possible.
- The risk from the radiation is minimal, and it dissipates from the body within a few hours.
3. Reviewing Scan Results:
-
- Your doctor or a radiologist will review the series of images from your scan.
- An appointment will be scheduled to discuss the findings, where they’ll explain any abnormalities or confirm the absence of bone-related problems.
- Based on the results, further tests or treatment procedures may be advised if necessary.
Following these post-scan instructions will ensure a smooth end to your nuclear medicine procedure. It will prepare you for the next steps in your healthcare journey.
Choose PRP Diagnostic Imaging for Expert Nuclear Medicine Procedures

In the hands of PRP Diagnostic Imaging’s experts, nuclear medicine procedures are extremely safe, accurate, and crucial for the evaluation of various bone diseases and disorders.
If you have any questions or need clarity on anything related to bone scans or nuclear medicine in general, don’t hesitate to reach out.
Choose PRP Diagnostic Imaging for your diagnostic needs. Get in touch with your local clinic today.
