
The Differences Between Nuclear Medicine & Radiology
Nuclear medicine or radiology — what’s the difference?
They’re two distinct imaging techniques with their own strengths in diagnosing and treating conditions. Understanding these differences empowers patients and healthcare providers to choose the best technique for each case.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the unique aspects of nuclear medicine and radiology and cover everything you need to know.
If you need immediate medical advice, PRP Diagnostic Imaging is a leader in providing diagnostic imaging services in New South Wales. Reach out to us today for expert, patient-centred care.
What is Radiology?
Radiology is a medical specialty that uses imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases within the body. Let’s take a closer look:
Types of Radiology Procedures
- X-ray: Quick tests that produce images of the structures inside the body, particularly the bones.
- CT (Computed Tomography): Advanced imaging that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body, helping diagnose a range of conditions.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues.
- Ultrasound: Medical sound waves used to produce images, instrumental in obstetrics and for imaging soft tissues.
Role of a Radiologist
Radiologists are medical doctors who specialise in interpreting medical images. They play a crucial role in diagnosing conditions and guiding treatment plans.
Common Uses
Radiology is pivotal in diagnosing a wide range of conditions, from identifying tumours and broken bones to monitoring disease progression.
PRP Imaging Radiology Services
- Cardiac
- Mammography
- MRI
- Ultrasound
- X-ray
Radiology services at PRP Diagnostic Imaging offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, leading to precise and early detection of health issues for our patients.
What is Nuclear Medicine?
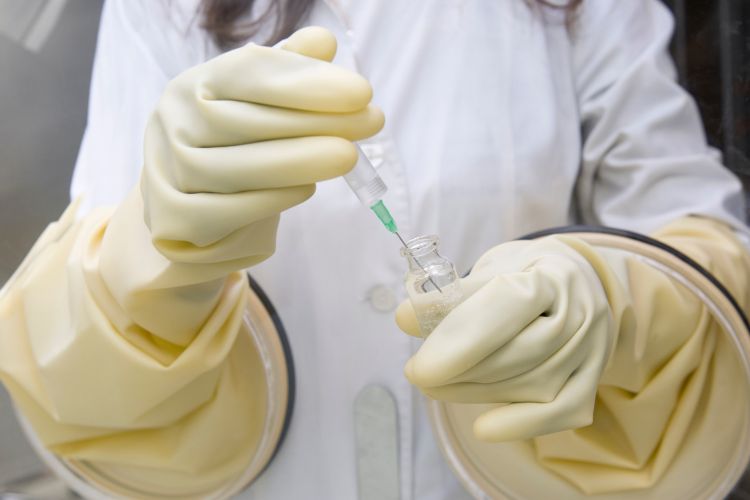

Nuclear medicine is a branch of medical imaging that uses small amounts of radioactive isotopes to diagnose and treat diseases. Here’s an overview:
Types of Nuclear Medicine Tests
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography): Provides detailed images of the body’s biological functions, helping to identify diseases like cancer.
- SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography): Uses three-dimensional images to observe organ function.
Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
Radioactive isotopes are most commonly introduced to the body via an injection, though sometimes they can be ingested. These isotopes emit energy that is detected by special cameras, creating images that show organ and tissue function.
Therapeutic Applications
Beyond diagnosis, nuclear medicine is used in treatments, notably for thyroid cancer and hyperthyroidism. These treatments use radioactive iodine. The newest prostate therapy uses lutetium-177 for prostate-specific membrane antigen (PMSA) therapy.
PRP Imaging Nuclear Medicine Services
- Bone Scan
- Myocardial Perfusion Scan
- Thyroid Scan
- V/Q Lung Scan
- White Blood Cell Scan
- PET (FDG/PSMA/Dotatate)
- Renal
- Biliary
- Parathyroid
Nuclear medicine at PRP Diagnostic Imaging leads to the early detection and assessment of the body’s organ function. It’s a crucial tool for both diagnosis and treatment.
The Differences Between Nuclear Medicine and Radiology
If we want to understand the roles of nuclear medicine and radiology in healthcare, we need to look at their differences.
Technology and Techniques
- Nuclear Medicine: Uses radioactive isotopes to assess organ function and structure.
- Radiology: Uses X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasounds to visualise internal structures of the body.
Use in Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
- Nuclear Medicine: Ideal for detecting and treating certain diseases at early stages by examining organ function.
- Radiology: Suited to identify structural abnormalities and guide the treatment of different diseases.
Radiopharmaceuticals vs. Contrast Injections
- Nuclear Medicine: Uses radiopharmaceuticals that target specific organs or tissues, emitting radiation from within the body.
- Radiology: Uses contrast injections to enhance the clarity of images of the body.
Imaging Results and Patient Health Insights
- Nuclear Medicine: Reveals how well organs and tissues are functioning, offering early disease detection.
- Radiology: Provides detailed images of the anatomy, helping diagnose conditions based on structural appearance.
High-Level Considerations When Choosing Between Nuclear Medicine and Radiology
Choosing the right imaging procedure requires careful consideration. Here are some factors that our medical professionals look at:
Nature of the Medical Condition
Medical professionals will consider whether the condition affects structure or function. Nuclear medicine is unparalleled in imaging organ function and detecting diseases early, while radiology helps us visualise any structural abnormalities.
Risks Associated
Nuclear medicine involves radioactive material but poses very minimal risks due to the low exposure levels. It requires specialised handling by nuclear medicine technologists.
Radiology techniques, particularly those using ionising radiation (like X-rays and CT scans), also carry minimal exposure risks. Technologists use the minimum level of radiation exposure possible to maximise the procedure’s safety.
Availability and Costs
You and your doctor will consider the availability of specific imaging procedures and their costs. Nuclear medicine may not be available everywhere, and can be more expensive than standard radiology services.
Choosing the right procedure depends on these key considerations. Whether you need a nuclear medicine technologist or a radiologist, PRP Diagnostic Imaging ensures the most effective and appropriate care for you and your needs.
Pros & Cons: Radiology
Pros:
- Wide Availability: Services like X-rays and CT scans are widely accessible, providing crucial imaging in various areas of medicine, such as oncology and angiography.
- Efficiency and Cost: These exams are generally faster and less expensive than nuclear medicine procedures, making them a practical choice for many patients.
- Non-Invasive: These procedures are non-invasive. They use advanced equipment to capture detailed pictures of structures like the brain and heart.
Cons:
- Radiation Exposure: Despite the minimal amount of ionising radiation used thanks to modern equipment, exposure is still a consideration, particularly for patients who are nervous about radiography or undergoing repeated exams.
- Sensitivity Limitations: While excellent for structural imaging, radiology might not match the sensitivity of nuclear medicine in identifying certain types of diseases, especially in the early stages.
- Functional Imaging: Radiology’s capability for functional imaging is limited compared to nuclear medicine. Nuclear medicine techniques like using a gamma camera can offer dynamic pictures of how the organs and tissues function, using a tracer administered via injection into a vein, which is a capability beyond the scope of standard radiography.
Pros & Cons: Nuclear Medicine
Pros:
- Functional Insights: Provides valuable information about the function and condition of organs and tissues beyond just the physical image. This is crucial for certain areas of diagnosis and treatment.
- Early Detection: Highly sensitive to changes at the cellular level, nuclear medicine can detect abnormalities and diseases in their early stages, often before they’re visible through other imaging processes.
- Dual Purpose: Unique among imaging types, nuclear medicine serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It uses radiopharmaceuticals to target and treat conditions directly — for example, thyroid cancer.
Cons:
- Safety Concerns: The use of radioactive materials, while carefully regulated and generally very safe, may raise concerns or anxieties regarding exposure and potential damage. Certification and strict safety standards are in place to minimise risks.
- Cost and Time: Procedures can be more expensive and time-consuming compared to standard radiological exams. This is partly due to the specialised equipment like gamma cameras and tracers required.
- Accessibility: The availability of nuclear medicine services can be limited in some regions, restricting access to these advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options for some patients.
Making Informed Choices
Your physician will assess your situation closely when choosing between radiology and nuclear medicine. However, radiology and nuclear medicine often work best when they work together. To get the best, most detailed results, your doctor may wish to use a combination of scans.
Radiology excels in detailing anatomical structures, using exams like X-rays and MRI to identify fractures and other structural changes.
Nuclear medicine, with tracers and specialised scanners, provides critical functional insights into cells and organ systems. It aids in early disease detection and treatment.
Your physician’s decision will be based on the type of information needed — structural or functional, the specific area of concern, and your overall health condition. For example, PET scans in nuclear medicine are invaluable for assessing cancer, while radiology is often used to identify fractures.
At the end of the day, you should always consult with your physician. They can offer personalised advice and consider the number of factors at play. They’ll guide you through your options and address any questions or concerns about the exam process, whether it involves a radiopharmaceutical for nuclear medicine or a traditional imaging scanner for radiology.
Radiology or Nuclear Medicine Tailored to Your Healthcare Needs
PRP Diagnostic Imaging is here to help you and provide a personalised healthcare plan, no matter what you’re facing.
We offer a range of imaging services. From detailed examinations using tracers to visualise blood flow to addressing specific needs like back pain, breast health, or injections, our services are designed with your well-being at the forefront.
Our team’s advanced training and certifications ensure precise and compassionate care, whether we use radiology or nuclear medicine.
Want to learn more about how our services can be part of your health story? Book an appointment for a professional consultation today and find the imaging test that’s right for you.
For further information, visit our nuclear medicine services page.
